The traditional divide between customer-facing operations and internal business processes is dissolving. AI agents are emerging as the catalysts for this transformation, creating seamless connections between front-office customer relationship management (CRM) systems and back-office enterprise resource planning (ERP) operations. This convergence represents more than technological advancement—it points to a fundamental shift in how businesses operate, make decisions, and serve customers.
The Evolution Beyond Traditional Business Silos
Enterprise operations have historically functioned in distinct compartments. Sales teams worked within CRM platforms, finance departments operated ERP systems, and human resources managed separate training modules. Each system generated valuable data, but extracting insights across these boundaries required manual intervention and complex integrations.
AI agents are dismantling these barriers by acting as intelligent intermediaries that understand context, make autonomous decisions, and execute tasks across multiple systems. Unlike simple automation tools that follow predetermined rules, these agents adapt their behavior based on real-time data and environmental feedback.
How AI Agents Transform Customer-Facing Operations
Predictive Customer Intelligence
AI agents within CRM systems now leverage historical customer data to predict future behaviors and preferences. These systems analyze purchase patterns, engagement metrics, and communication histories to generate personalized recommendations that extend far beyond basic demographic targeting.
The predictive capabilities enable organizations to anticipate customer needs before explicit requests arise. AI can draw in potential customers with its highly personalized experiences. The AI can analyze customer data through algorithms and recommend products or services that are individualized based on that customer’s needs.
Automated Lead Qualification and Scoring
Modern AI agents excel at evaluating lead quality by processing multiple data points simultaneously. Teams can prioritize leads more efficiently and assess the likelihood to convert with AI-driven lead scoring. Factors such as demographics and behavior help salespeople target the best leads, increasing overall sales and upselling.
This capability extends beyond simple scoring algorithms. AI agents continuously refine their evaluation criteria based on successful conversion patterns, creating dynamic qualification processes that improve over time.
Real-Time Sentiment Analysis
Social media monitoring and customer feedback analysis have evolved from periodic reviews to continuous assessment streams. AI agents now track sentiment across multiple channels, enabling immediate response to customer concerns and identifying emerging trends that impact brand perception.
Revolutionizing Back-Office Operations Through Intelligent Automation
Financial Process Automation
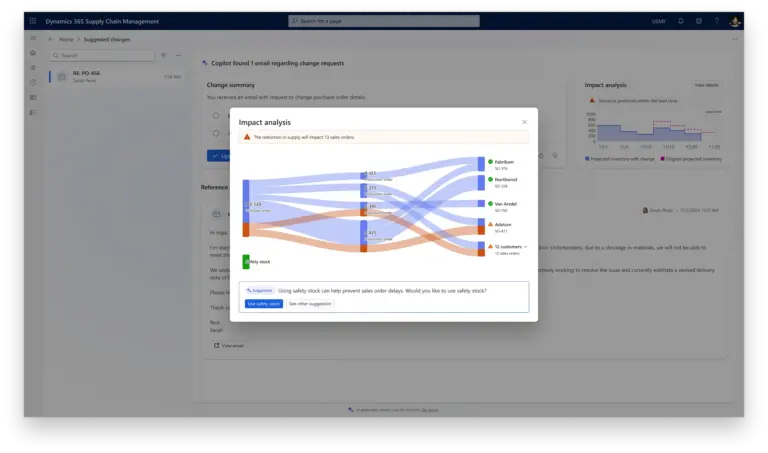
ERP systems enhanced with AI agents are transforming traditionally labor-intensive financial operations. The Account Reconciliation Agent exemplifies this shift by “accelerating the period-end close by matching ledger entries, flagging discrepancies, and recommending resolution steps.”
Microsoft customer Lifetime Products demonstrated immediate process improvements after deploying such automation. Ted Esplin, COO of Lifetime Products, noted: “Using AI and autonomous agents are just the next level for us when it comes to realizing the full benefit of our Dynamics 365 environment.”
Supply Chain Intelligence
The Supplier Communications Agent represents a significant advancement in supply chain management by “acting instantly on supplier emails, chasing missing order confirmations and delayed shipments. By closing the loop on every critical supplier touchpoint, the agent slashes rush charges, prevents costly disruptions, and protects your margins.”
Expense Management Optimization
Traditional expense reporting has been reimagined through AI agents that “extract key details from receipts—such as vendor, amount, date, and category—and intelligently suggest classifications aligned with company travel and expense policies.” This automation ensures policy compliance while reducing administrative burden across finance teams.
The Convergence: Where CRM Meets ERP
The most significant transformation occurs when AI agents facilitate seamless information flow between customer-facing and internal operations. This convergence manifests in several critical ways:
Unified Customer Data Ecosystems
AI agents aggregate customer information from CRM touchpoints and correlate it with operational data from ERP systems. This unified view enables organizations to understand the complete customer lifecycle, from initial engagement through order fulfillment and ongoing support.
Dynamic Resource Allocation
When AI agents detect patterns in customer demand through CRM analysis, they can automatically trigger resource adjustments in ERP systems. This might involve inventory reallocation, production scheduling modifications, or supply chain optimization based on predicted customer behavior.
Integrated Financial Intelligence
Customer acquisition costs, lifetime value calculations, and profitability analysis now happen in real-time as AI agents connect sales data with operational expenses and resource utilization metrics.
Organizational Learning and Skill Development
Personalized Employee Training
The impact of AI agents extends beyond operational systems to workforce development. Companies like Uplimit are rolling out educational AI agents that promise significantly higher completion rates (upwards of 90 percent) and better results.
Bill Gates captured the potential of personalized learning when he explained: “If a tutoring agent knows that a kid likes Minecraft and Taylor Swift, it will use Minecraft to teach them about calculating the volume and area of shapes, and Taylor’s lyrics to teach them about storytelling and rhyme schemes.”
This personalization principle applies equally to corporate environments, where AI agents tailor training content to individual learning styles, job responsibilities, and career development goals.
Accelerated Skill Acquisition
The clearest advantage of using AI agents for training is faster, more effective learning. Agents can train a higher volume of employees in the same amount of time. This efficiency gain becomes crucial as organizations adapt to rapidly changing market conditions and technological requirements.
Implementation Patterns and Best Practices
Workflow-Based Approaches
Successful AI agent implementations often begin with workflow-based systems where “LLMs and tools are orchestrated through predefined code paths.” These provide predictability and consistency for well-defined tasks before evolving toward more autonomous agent behaviors.
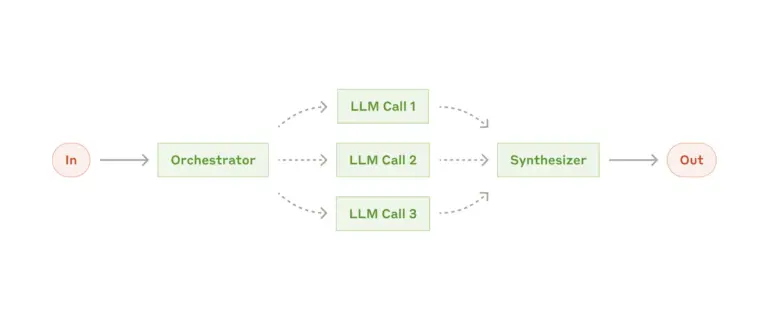
Orchestrator-Worker Models
Complex business processes benefit from orchestrator-worker architectures where “a central LLM dynamically breaks down tasks, delegates them to worker LLMs, and synthesizes their results.” This pattern proves particularly effective for processes that span multiple business functions.
Tool Design and Integration
The success of AI agents depends heavily on thoughtful tool design. “One rule of thumb is to think about how much effort goes into human-computer interfaces (HCI), and plan to invest just as much effort in creating good agent-computer interfaces (ACI).”
Measurable Business Impact
Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Organizations implementing AI agents across CRM and ERP systems report significant operational improvements. AI can not only process and analyze data quickly, but it can also complete repetitive tasks with greater speed and efficiency than human employees typically can. This means that tasks are completed faster, and employees are free to focus on more strategic work that drives business growth and success.
Enhanced Decision-Making Capabilities
AI can be a great tool to enable data-driven decisions by leveraging advanced algorithms, machine learning, and data analysis to extract meaningful insights from large amounts of structured and unstructured data. This capability becomes exponentially more powerful when applied across integrated CRM-ERP environments.
Improved Customer Experience
The convergence of front-office and back-office systems through AI agents creates unprecedented customer service capabilities. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle high volumes of customer requests and provide personalized responses to quickly meet customer needs—especially when answering simple queries that support teams frequently get.
Challenges and Implementation Considerations
Integration Complexity
Integrating AI into existing tech stacks and IT infrastructure can be complex. Ensuring that new AI tools work well with legacy systems is crucial for the success of AI automation. Organizations must carefully plan integration strategies that respect existing investments while enabling new capabilities.
Data Security and Privacy
As AI agents access and process information across multiple systems, data protection becomes paramount. AI systems rely heavily on data to work well. But it’s important to make sure that sensitive business and customer data are protected.
Change Management
Employees might be hesitant to embrace AI automation due to fears of losing their jobs or simply because they’re unfamiliar with the technology. Successful implementations require comprehensive change management strategies that position AI agents as enhancement tools rather than replacement technologies.

Data-driven and data-informed decision making processes are the key in efficient business practices. Image credit: senivpetro via Freepik, free license
Future Implications and Emerging Trends
AI-Driven Personalization Evolution
AI is improving customer service through hyper-personalization. By analyzing customer data, AI can offer individualized product recommendations and provide tailored support, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
IoT Integration Expansion
The Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly integrated with AI to enable smarter devices and systems. This combination has the potential to revolutionize industries like manufacturing, where AI-driven IoT devices can monitor equipment, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production.
Strategic Decision Automation
More businesses are using AI to support strategic decision-making. With AI’s ability to process data and predict trends, decision-makers can now rely on AI to guide their business strategies.
Getting Started: A Practical Roadmap
Phase One: Assessment and Pilot Programs
Organizations should begin by evaluating which tasks are most repetitive and time-consuming for you and your team. Focus on processes where AI can add the most value, like customer service, inventory management, or data analysis.
Phase Two: Tool Selection and Training
Choose the right AI tools and platforms. With so many AI tools on the market, it can be difficult to choose the right platform for your needs. It’s important to carefully evaluate specific needs before choosing the tools that best align with your goals.
Phase Three: Gradual Scaling
Start with small pilot projects to test the technology and make adjustments before scaling up. This approach minimizes risk while building organizational confidence and expertise.
The Path Forward
AI agents represent more than technological innovation—they embody a fundamental reimagining of business operations. By dissolving the boundaries between customer-facing and internal systems, these agents create unprecedented opportunities for efficiency, insight, and customer value creation.
Organizations that embrace this convergence thoughtfully, addressing implementation challenges while maximizing integration opportunities, position themselves for sustainable competitive advantage. The question is not whether AI agents will transform business operations, but how quickly organizations can adapt their structures, processes, and cultures to harness this transformative potential.
The future belongs to enterprises that view AI agents not as isolated tools but as connective tissue that binds disparate business functions into cohesive, intelligent ecosystems. In this future, the boundaries between front-office and back-office operations become invisible, creating seamless experiences for customers and unprecedented operational insights for business leaders.
If you are interested in this topic, we suggest you check our articles:
- The Intersection of AI and Quantum Computing
- Neuromorphic Computing: Learn About AI Mimicking the Human Brain
- Rapid AI Development: 3 Key Reasons
Sources: Forbes, IBM, Microsoft, Anthropic, Rippling, IBM(2)
Written by Alius Noreika