Key Facts at a Glance: ChatGPT Atlas
- Contextual AI Sidebar: Access real-time ChatGPT assistance on any webpage without switching tabs or copying content
- Autonomous Agent Mode: Delegate multi-step tasks like research, booking, and shopping to AI that navigates sites independently
- Browser Memory System: AI remembers browsing context across sessions, retrieving past research and continuing interrupted tasks
- In-Line Text Assistance: Highlight text anywhere to generate, edit, or improve content directly within form fields
- Conversational Search Interface: Query using natural language instead of keywords, receiving AI-generated summaries with source links
- Cross-Session Task Continuity: Resume projects from days or weeks ago with full context automatically restored
- Privacy-First Architecture: Granular controls including site-specific memory toggles, incognito mode, and transparent data handling
- Chromium-Based Stability: Built on trusted framework ensuring compatibility with modern web standards
- Premium Features: Agent mode and advanced capabilities require ChatGPT Plus, Pro, or Business subscriptions
- Platform Availability: Currently macOS only, with Windows, iOS, and Android versions coming soon
OpenAI has launched ChatGPT Atlas, an artificial intelligence-powered browser that transforms web navigation from passive consumption to active collaboration. Unlike Chrome, Safari, or Firefox, Atlas integrates ChatGPT directly into every aspect of browsing, creating capabilities impossible in traditional browsers. The tool represents a fundamental shift: instead of simply displaying websites, Atlas understands them, remembers them, and acts on them.
Traditional browsers excel at speed and compatibility but require users to manually perform every action. ChatGPT Atlas changes this dynamic by embedding an AI assistant that participates in browsing rather than observing it. Built on the Chromium framework for stability, Atlas adds layers of intelligence that make web navigation intuitive, contextual, and autonomous.
The Architecture Behind ChatGPT Atlas Innovation
ChatGPT Atlas constructs its capabilities on three foundational technologies. The browser uses the Chromium engine to ensure compatibility with modern web standards and extensions. OpenAI has integrated ChatGPT’s language models directly into the browsing layer, creating persistent context between the assistant and webpage content. The system employs a memory architecture that stores contextual insights rather than simple history lists, enabling the AI to understand browsing patterns and user intent.
This architecture enables capabilities that traditional browsers cannot replicate through extensions or plugins. The tight integration between browsing engine and AI assistant creates a unified experience where intelligence operates at the browser level rather than as an add-on.
1. Contextual AI Sidebar With Continuous Awareness
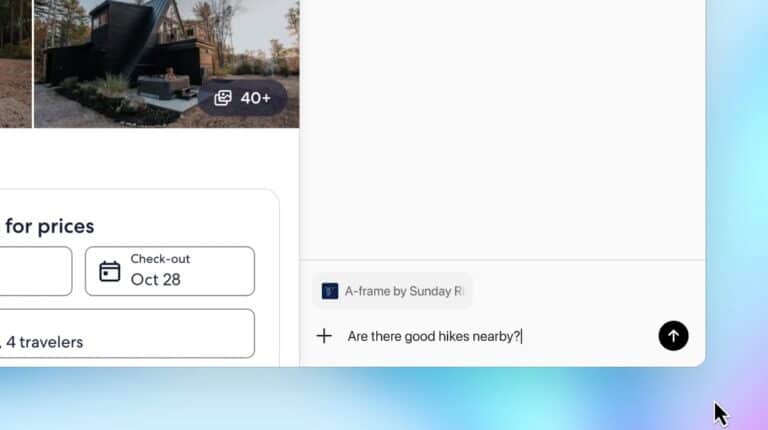
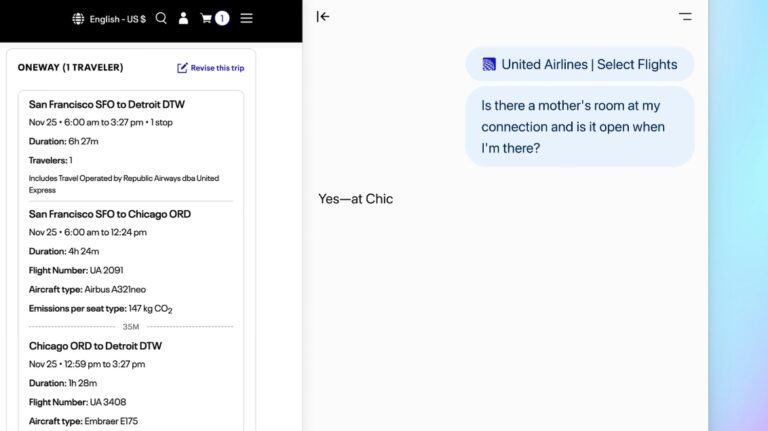
The Ask ChatGPT sidebar represents the most immediate departure from traditional browsing. This persistent panel appears alongside any webpage, providing instant access to AI assistance without disrupting your current view. Chrome extensions offer chatbot integration, but they lack direct access to page content and require manual input.
ChatGPT Atlas sidebars automatically understand the current webpage context. When visiting a technical article, you can request clarifications of complex terminology or summaries of key arguments. On shopping sites, the sidebar offers to compare products, highlight deals, or analyze specifications. The AI reads page content directly, eliminating the need to copy and paste information between windows.
Users can ask questions like finding all job postings viewed last week and creating summaries of industry trends for interview preparation, with ChatGPT drawing from browsing context automatically. This contextual awareness extends beyond the current page to your entire browsing history, creating an assistant that understands not just what you’re viewing but what you’ve been researching.
The sidebar maintains conversation continuity across pages. Start a discussion about renewable energy on one site, navigate to another, and the conversation continues with accumulated context. Traditional browsers force users to restart conversations when switching tabs or reopen chatbot windows, breaking the flow of research.
2. Autonomous Agent Mode For Multi-Step Task Execution
Agent Mode transforms Atlas from a passive viewer into an active participant in web tasks. Available in preview for Plus, Pro, and Business users, agent mode allows ChatGPT to take actions in your browser, including researching, analyzing, automating tasks, and planning events or booking appointments. This capability operates at a different level than browser automation scripts or macros.
When activated, Agent Mode receives your instructions in natural language and executes them by navigating sites, clicking links, filling forms, and extracting information. Request help planning a dinner party, and the agent opens recipe pages, identifies ingredients, navigates to a grocery delivery service, and adds items to your cart. Ask for competitive research on software products, and it visits multiple vendor sites, compares features, and compiles findings.
The agent can plan dinner parties by putting recipes together, or compare multiple websites and analyze their differences in a slide deck, opening tabs, reading content, pulling information, and formatting results. Traditional browsers require users to manually perform each of these steps or rely on brittle automation tools that break when website layouts change.
The system implements multiple safeguards. ChatGPT cannot run code in the browser, download files, or install extensions, and it pauses to ensure users watch actions taken on sensitive sites like financial institutions. Agent Mode cannot access your computer’s file system or other applications, maintaining security boundaries that protect user data.
The technology remains in preview because complex workflows sometimes produce errors. OpenAI continues improving reliability and task success rates, but current capabilities already exceed what traditional browsers offer. No other mainstream browser enables AI to autonomously navigate sites and complete multi-step processes under user supervision.
3. Browser Memory That Reconstructs Research Context
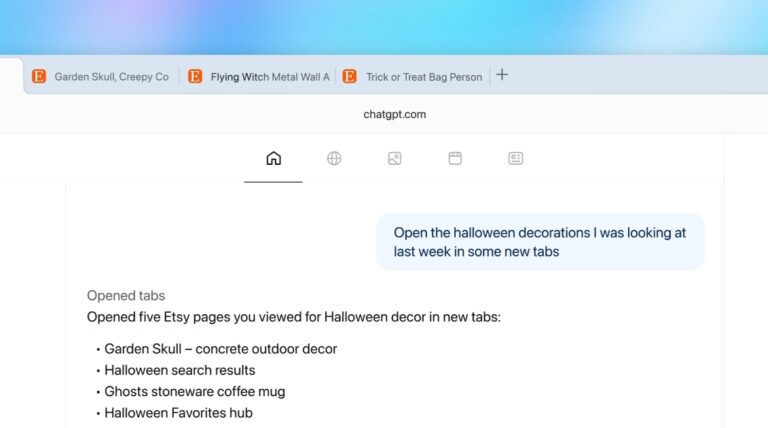
Browser Memory distinguishes ChatGPT Atlas from both traditional browsers and other AI assistants. The system stores contextual insights rather than simple history lists, remembering details like researching tax software last week, comparing three hotels and saving two tabs, or beginning a business plan and reviewing four example templates. This contextual storage enables capabilities impossible with standard browsing history.
Users can later issue commands in natural language: “Resume my research on Greek hotels” or “Open the business plan draft from last week.” Atlas reconstructs relevant tabs and context automatically. Chrome’s history shows a chronological list of URLs. ChatGPT Atlas understands the projects and research threads connecting those pages.
The memory system operates on an opt-in basis with complete user control. Users can view all memories in settings, archive ones no longer relevant, and clear browsing history to delete associated memories. Even with memory enabled, users can decide which sites ChatGPT can or cannot see using the toggle in the address bar, and when visibility is off, ChatGPT cannot view page content and no memories are created.
This capability creates continuity across browsing sessions that traditional browsers cannot match. Research that spans days or weeks maintains coherence because the AI understands not just what sites you visited but why you visited them and what you were trying to accomplish.
4. In-Line Writing Assistance For Direct Content Creation
Atlas embeds ChatGPT into text input fields across the web, creating in-line writing assistance unavailable in standard browsers. Users can pull up ChatGPT in any form field to write or edit without switching tabs, highlighting text inside the form field or document and clicking the ChatGPT logo. This integration eliminates the workflow disruption of composing text in a separate application.
The feature operates contextually. When drafting an email, the assistant understands you’re writing correspondence and adjusts suggestions accordingly. In comment fields, it recognizes the conversational tone required. For professional documents, it maintains appropriate formality. Traditional browsers require switching to external applications or browser tabs to access writing assistance.
After generating or editing text, users can refine output through conversational commands. “Make this more concise” or “Adopt a friendlier tone” produces immediate revisions without leaving the input field. The interface includes an Update button that applies changes directly, streamlining the editing process.
This capability extends beyond simple text generation. Users can highlight existing text on any webpage and invoke ChatGPT to summarize, explain, translate, or rewrite the content. In-line writing help allows highlighting text in any form field and calling ChatGPT to edit or improve sentences without switching tabs. Chrome extensions cannot replicate this deep integration with page elements.
5. Conversational Search That Understands Intent
Atlas replaces keyword-based search with conversational queries that understand user intent. The new tab page serves as a starting point where users can ask questions in natural language rather than constructing search terms. Users can ask a question or enter a URL to see faster, more useful results in one place, with options to explore specific result types through tabs for search links, images, videos, and news.
The system generates AI summaries alongside traditional search results. Instead of visiting multiple sites to understand a topic, users receive synthesized information with source links for verification. When researching complex subjects, this approach reduces the time spent gathering information from scattered sources.
ChatGPT remembers previous searches and browsing context when interpreting new queries. ChatGPT can remember what users have explored and suggest what to do next, whether returning to past pages, digging deeper into a topic, surfacing related ideas, or automating routine tasks. A query about “the hotel I was looking at” makes sense to ChatGPT Atlas because it understands your recent browsing activity. Google requires precise searches because it lacks this contextual awareness.
The interface adapts to different search needs. Users can toggle between AI-enhanced results and traditional web results depending on whether they want synthesized information or direct access to source material. This flexibility makes ChatGPT Atlas suitable for both quick factual queries and in-depth research.
6. Cross-Session Task Continuity With Project Understanding
ChatGPT Atlas keeps awareness of ongoing projects across multiple browsing sessions, creating continuity that traditional browsers cannot provide. The ChatGPT browser memory learns from browsing patterns to deliver increasingly relevant search suggestions, contextualizing queries based on previous searches, frequently visited sites, and interaction history. This creates an assistant that understands not just isolated queries but extended research efforts.
Users can interrupt work and resume days later with full context restored. “Continue the competitor analysis I started Wednesday” retrieves relevant tabs, previous findings, and research direction without requiring manual reconstruction. Chrome’s session restore reopens tabs but provides no understanding of why those tabs were open or what task they served.
The system identifies patterns in browsing behavior to make proactive suggestions. After visiting several articles about machine learning frameworks, Atlas might suggest creating a comparison document or finding implementation tutorials. These suggestions emerge from understanding research intent rather than simple pattern matching.
Project continuity extends to complex multi-day tasks. Planning a vacation involves researching destinations, comparing flights, evaluating hotels, and identifying activities. ChatGPT Atlas maintains context across these phases, allowing users to reference earlier research without manually tracking every page visited. Traditional browsers treat each session as isolated, forcing users to remember or reconstruct their research journey.
7. Privacy Architecture With Granular Site Control
Atlas implements privacy controls that exceed traditional browser capabilities while enabling AI features. Users can clear history for specific pages or entire history altogether, and can open incognito windows where they are signed out of ChatGPT and chats and memory are not saved to their account. These basic privacy features match standard browsers.
The distinctive capability lies in granular control over AI access. Even when browser memories are enabled, users can decide which sites ChatGPT can or cannot see using the toggle in the address bar, and when visibility is off, ChatGPT cannot view page content and no memories are created. This site-specific control allows users to enable AI assistance for research while blocking it from sensitive pages like banking sites.
By default, OpenAI does not use browsing content to train models, though users can opt-in by enabling “include web browsing” in ChatGPT Atlas data controls settings. This default-off approach to training contrasts with services that automatically use user data for model improvement.
Parental controls integrate with ChatGPT’s existing supervision features. If parents have set up parental controls for ChatGPT, these settings carry over to Atlas conversations, with new Atlas-specific controls including options to turn off browser memories and agent mode. Traditional browsers offer content filtering but lack these AI-specific protections.
The transparency of memory storage allows users to audit what information the system retains. All memories appear in settings where users can view, archive, or delete individual entries. This visibility ensures users maintain control over their data rather than trusting opaque systems.
8. Natural Language Command Execution For Browser Control
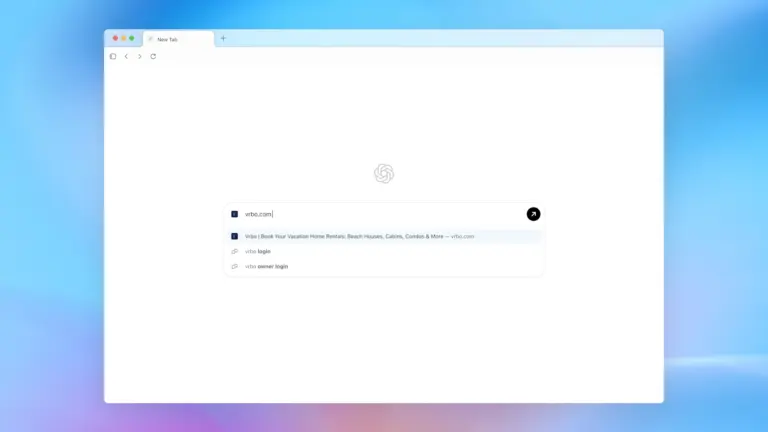
ChatGPT Atlas starts with the new tab page as your central command hub. Submit queries or web addresses to receive consolidated, efficient results instantly. For targeted exploration beyond conversational responses, switch between dedicated tabs displaying traditional links, visual content, video resources, and current news coverage depending on availability. Image credit: OpenAI
ChatGPT Atlas accepts plain English commands for browser control, eliminating the need to navigate menus or remember keyboard shortcuts. Users can say “Reopen that recipe I viewed yesterday” and Atlas will check web history and execute the command. Traditional browsers require manual history searches or tab restoration.
The system understands temporal references and contextual queries. “Show me the articles I read this morning about renewable energy” or “Find that LinkedIn profile I visited last week” work because Atlas comprehends both time references and subject matter. Chrome’s search history requires exact URL fragments or page titles.
Navigation commands operate conversationally. “Take me to the Wired website” opens the destination without requiring users to type URLs or search. “Open my last five closed tabs” restores recent work immediately. These natural language interactions reduce the cognitive load of browser management.
The capability extends to complex multi-step operations. “Find all the product comparison pages I opened yesterday and create a summary document” triggers a sequence of actions: locating relevant pages in history, extracting key information, and compiling results. Traditional browsers would require users to manually perform each step.
Command execution works across different browser functions. Users can request downloads, bookmark management, tab organization, and settings changes through conversation rather than interface navigation. This accessibility particularly benefits users who struggle with complex menu hierarchies or keyboard shortcuts.
9. Multi-Format Search Integration With Intelligent Routing
ChatGPT Atlas provides unified access to multiple search formats through a single interface. Users can search text, images, videos, or news articles, using tabs, autocomplete, a search bar, and bookmarks to navigate the web easily. The innovation lies not in offering multiple search types but in how the AI routes queries to appropriate formats.
When users ask “latest developments in quantum computing,” Atlas determines whether text articles, academic papers, or video explanations best serve the query. The AI-generated response might combine information from multiple formats, presenting a comprehensive overview with links to detailed sources in each category.
The system supports custom search shortcuts for frequently used platforms. Users can configure direct searches for specific sites like Amazon, Wikipedia, or Netflix, streamlining access to specialized information. Users can customize shortcuts for site-specific searches, allowing direct queries on platforms to save time and effort. While traditional browsers offer similar shortcuts, Atlas combines them with AI understanding that interprets intent.
Search results appear with AI-generated context. Instead of a list of blue links, users receive explanations of how each result relates to their query and which sources provide the most relevant information. This curation reduces time spent evaluating search results and identifying authoritative sources.
The format integration extends to mixed-media queries. Ask “show me before and after photos of home renovations and explain cost considerations” and Atlas retrieves images while generating cost analysis text. Traditional search requires separate queries for different information types.
10. Automated Form Interaction With Context Awareness
Atlas automates form filling with intelligence beyond traditional autofill. The system can save addresses, passwords, and payment information like standard browsers, but adds an AI-powered understanding of form context. Atlas can save and autofill addresses, passwords, and payment cards, with settings to turn autofill on or off for each category.
The distinctive capability emerges in complex forms that require contextual understanding. When filling applications, Atlas can reference your browsing history and stored information to complete fields intelligently. Instead of manually copying information from documents, users can instruct the AI to extract relevant data and populate forms.
The system understands form relationships that simple autofill misses. If a website asks for shipping addresses, billing addresses, and contact information, ChatGPT Atlas recognizes these as related but distinct fields requiring different data. Traditional autofill often inserts the same information into all address fields regardless of context.
Payment integration goes beyond stored credit cards. Atlas recognizes wallet buttons for services like PayPal and Shop Pay provided by websites, integrating these payment options into the form completion process. The AI can guide users through checkout processes, suggesting the most efficient payment method based on available options.
Form interaction extends to automated data extraction. When researching products, Atlas can capture specifications, pricing, and availability information into structured formats without manual copying. This capability streamlines comparison shopping and research documentation tasks that consume significant time in traditional browsers.
Technical Requirements and Limitations
ChatGPT Atlas currently operates only on macOS, with platform availability limited while Windows and mobile versions are in development. This restriction limits accessibility for many users who rely on other operating systems. OpenAI has announced expansion plans but provided no specific release dates.
The most powerful features require paid subscriptions. Agent mode is only available to ChatGPT users on Plus, Pro, and Business tiers at launch. Free users can access the sidebar and basic AI assistance but cannot use autonomous task execution. This tiered approach means the browser’s most compelling capabilities remain behind a paywall.
Early users report performance inconsistencies. Some features perform inconsistently, with the AI’s ability to provide contextual insights varying depending on task complexity or website content. Compatibility issues exist because certain websites block OpenAI services, limiting browser effectiveness in specific scenarios.
The browser lacks some standard features found in mature alternatives. Atlas currently lacks advanced functionalities like grouped tabs and support for multiple user profiles that are standard in many other browsers. These omissions affect users who rely on organizational tools for managing complex browsing workflows.
Security researchers have identified vulnerabilities. The browser is susceptible to prompt injection attacks where malicious URLs can trigger AI actions, and researchers demonstrated how crafted prompts disguised as URLs can jailbreak the omnibox. OpenAI continues addressing these security concerns but the integration of AI creates new attack vectors not present in traditional browsers.
Market Context and Competition
Atlas enters a competitive landscape that includes AI-powered browsers like Perplexity’s Comet, The Browser Company’s Dia, and Opera Neon, each offering built-in chatbots that sit in side panels with automatic context. Google has integrated Gemini into Chrome, while Microsoft added Copilot to Edge. These competitors demonstrate the broader industry trend toward AI-enhanced browsing.
OpenAI’s launch stands out because it potentially reaches 800 million weekly ChatGPT users, giving Atlas distribution scale that rivals cannot match. This existing user base provides a significant advantage in adoption potential, though converting ChatGPT users to Atlas users requires demonstrating compelling value.
The browser faces the dominant position of Google Chrome. Chrome holds approximately 71.9% of the browser market share as of September 2025. Displacing this entrenched leader requires not just feature parity but substantial advantages that motivate users to change established habits.
Business model questions remain unresolved. Analysts note that if OpenAI chooses to sell ads in Atlas, it could siphon advertising revenue from Google, with the browser giving OpenAI a direct channel to tie monetization to both web traffic and AI services. The current subscription-based approach limits revenue potential compared to advertising models that traditional search engines employ.
Privacy concerns create adoption barriers. Browsers gobble up users’ most sensitive information like passwords and credit card information, and law enforcement is already demanding ChatGPT user data, with warrants showing investigators requesting users’ ChatGPT histories as part of ongoing cases. These privacy implications require users to trust OpenAI with browsing data that they may not willingly share.
Future Development Trajectory
OpenAI continues developing ChatGPT Atlas with planned improvements addressing current limitations. The company is working on multi-profile support to enable different users or work contexts on the same device. An App SDK integration will allow calling other applications within ChatGPT, improving discoverability and extending functionality beyond web browsing.
Agent mode remains experimental, with OpenAI rapidly improving reliability, latency, and complex task success rates. As the technology matures, the browser will handle more sophisticated workflows and reduce the supervision required for autonomous task execution.
The memory system will become more sophisticated. Future versions may understand longer-term patterns and make predictive suggestions about research directions or workflow optimizations. The AI could identify when users repeatedly perform manual tasks that could be automated through Agent Mode.
Platform expansion to Windows, iOS, and Android will significantly increase potential user base. Mobile versions face particular challenges in adapting the interface to smaller screens while maintaining the power of desktop capabilities. OpenAI must balance feature parity with platform-appropriate design.
Security improvements will address identified vulnerabilities. As researchers discover attack vectors specific to AI-powered browsers, OpenAI must implement defenses that protect users without limiting legitimate functionality. This balance between capability and security remains an ongoing challenge.
Practical Applications for Different User Types
Researchers benefit from the contextual memory and cross-session continuity. Academic work often spans weeks or months, requiring synthesis of information from dozens of sources. Atlas retains awareness of research threads, allowing scholars to ask questions like “summarize the methodology differences between the three papers I read about neural networks last week.”
Content creators use in-line writing assistance and the sidebar for drafting and editing. Writers can research topics while simultaneously generating content, with the AI understanding both source material and creative intent. The ability to refine text through conversation rather than manual editing accelerates content production.
Professionals conducting competitive intelligence leverage Agent Mode for automated research. Marketing teams can request competitor website analysis, feature comparisons, and market positioning assessments that the AI completes by visiting relevant sites and extracting information. This automation reduces time spent on repetitive research tasks.
Students useChatGPT Atlas for learning support. The sidebar can explain complex concepts encountered in online course materials, provide additional examples, or connect ideas across different subjects. Students mentioned using practice questions and real-world examples during lectures to understand material better. Atlas enables this active learning approach without disrupting the viewing experience.
Casual users benefit from simplified web navigation. Natural language commands and contextual assistance reduce the technical knowledge required for effective browsing. Users who struggle with traditional browser interfaces can accomplish tasks through conversation rather than menu navigation.
Strategic Implications for the Web
ChatGPT Atlas, in its essence, constitutes a shift from browsers as passive tools to active participants in web interaction. Traditional browsers serve content; Atlas interprets, acts upon, and remembers it. This transformation changes user expectations about what browsers should provide.
The technology challenges Google’s search dominance by positioning ChatGPT as the primary interface for information retrieval. Users spending time in Atlas may query ChatGPT instead of Google, potentially displacing search engine usage. This threat motivated Google and Microsoft to accelerate their own AI browser integrations.
Website design may evolve to accommodate AI consumption. If significant users access web content through AI assistants that summarize and extract information, site owners might optimize for machine readability rather than human visual experience. This shift could transform web design principles that have dominated for decades.
Privacy norms may change as users become comfortable with AI systems accessing browsing data. The transparency and control that Atlas provides could establish new standards for how AI assistants handle personal information. Alternatively, privacy concerns could limit adoption and push the industry toward more restrictive data practices.
The business model for web browsing faces disruption. If users increasingly access information through AI summaries rather than visiting sites directly, traditional advertising models lose effectiveness. New monetization approaches will emerge to support both browser developers and content creators.
ChatGPT Atlas introduces capabilities that traditional browsers cannot replicate, transforming web navigation from a manual process to an assisted collaboration with AI. The contextual sidebar, autonomous agent mode, persistent memory, and natural language control create an experience fundamentally different from Chrome, Safari, or Firefox.
These innovations come with significant limitations. Platform restrictions, subscription requirements, security vulnerabilities, and privacy concerns temper the potential impact. The browser remains in early development with inconsistent performance on complex tasks.
For users willing to accept these tradeoffs, Atlas offers genuine advantages in research continuity, task automation, and contextual assistance. The technology demonstrates how AI integration at the browser level creates capabilities impossible through extensions or add-ons. Whether Atlas achieves mainstream adoption depends on OpenAI’s ability to address current limitations while maintaining the innovative features that distinguish it from established competitors.
If you are interested in this topic, we suggest you check our articles:
- AI Agents Blur Business Boundaries
- Manus AI Agent: What is a General AI Agent?
- User Experience vs Agentic Experience: Designing for Delegation and Intent Alignment
- CustomGPT.ai: Genius Tool for Creating Custom AI Agents
Sources: OpenAI, Artificial Corner, Geeky Gadgets, BBC
Written by Alius Noreika